The Future of AR and VR in Mobile App Development
In the last decade, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have moved from experimental technologies to mainstream applications. With the launch of Apple Vision Pro (2024) and ongoing investments in Meta Quest and ARCore/ARKit frameworks, AR and VR are no longer just about gaming — they are transforming education, healthcare, retail, real estate, and mobile productivity.
For mobile app developers, this shift presents enormous opportunities. But it also raises questions: How do you integrate AR/VR into mobile apps? What industries will benefit most? And where is this technology heading in 2025 and beyond?
This article explores the current state and the future of AR and VR in mobile app development.
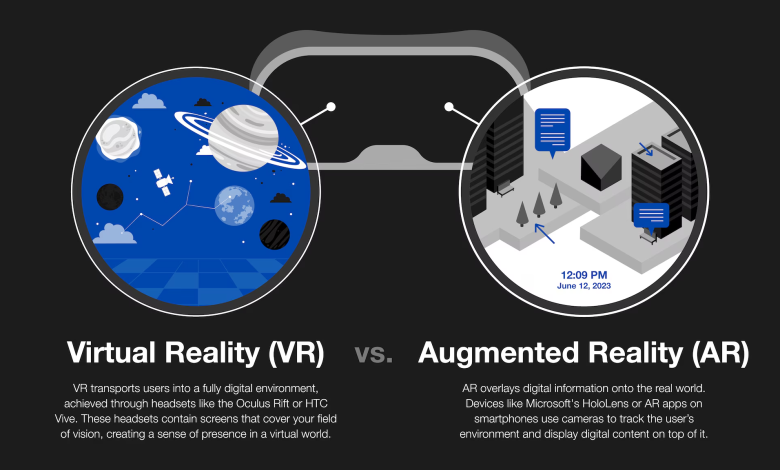
AR vs. VR: The Basics
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances the real world by overlaying digital objects (e.g., Pokémon Go, Snapchat filters).
- Virtual Reality (VR): Creates an entirely immersive, simulated environment (e.g., Oculus/Meta Quest apps, VR training simulations).
Mobile apps today often use AR more than VR due to accessibility (AR works on most smartphones with cameras), but VR adoption is growing with headsets becoming more affordable.
Why AR & VR Matter for Mobile Apps
Immersive Experiences
- Enhances user engagement by blending digital and physical worlds.
Business Value
- Real estate apps showcase 3D property tours.
- Retailers use AR for “try before you buy.”
New Interaction Models
- Gesture recognition, spatial mapping, and voice commands.
Market Growth
- The AR/VR market is expected to exceed $450 billion by 2030 (Statista).
Key Industries Using AR and VR
1. Gaming & Entertainment
- AR: Pokémon Go, Harry Potter Wizards Unite.
- VR: Beat Saber, immersive eSports.
2. Retail & E-Commerce
- AR-powered fitting rooms.
- IKEA Place lets users preview furniture at home.
3. Real Estate & Architecture
- VR tours of properties.
- AR overlays for construction plans.
4. Healthcare
- VR therapy for PTSD and anxiety.
- AR apps for surgical assistance.
5. Education & Training
- AR visualizations in science classes.
- VR simulations for pilot/medical training.
6. Travel & Tourism
- AR-guided tours of museums and historical sites.
- VR travel experiences.
AR/VR Development Frameworks
- ARKit (Apple): iOS AR development.
- ARCore (Google): Android AR experiences.
- Unity3D: Popular for VR/AR cross-platform apps.
- Unreal Engine: High-fidelity AR/VR applications.
- Vuforia: AR SDK with image recognition.
- Blender + 3D Assets: For building models and environments.
Challenges in AR/VR Mobile Development
Hardware Limitations
-
Mobile devices still limited in graphics and battery life.
High Development Costs
- Requires 3D design, motion tracking, and complex testing.
User Accessibility
- VR adoption depends on users owning headsets.
Performance & Latency
- AR/VR apps require low latency to avoid motion sickness.
Privacy Concerns
- AR apps collect sensitive environmental and spatial data.
Best Practices for Building AR/VR Mobile Apps
✅ Start with a clear use case (gaming, retail, education).
✅ Optimize for performance and battery efficiency.
✅ Use lightweight 3D assets and compress textures.
✅ Focus on usability — don’t overload users with complex gestures.
✅ Implement accessibility features (text-to-speech, scalable UI).
✅ Continuously test on different devices and lighting conditions.
Case Study: AR in Retail
A fashion brand launched an AR fitting-room app:
- Users could try on clothes virtually using their phone camera.
- Integrated with e-commerce checkout.
Results:
- Conversion rates increased by 20%.
- Return rates dropped by 15%.
The Future of AR and VR in Mobile Apps
Looking ahead, we’ll see:
Mixed Reality (MR) as the Norm
- Combining AR and VR into fluid, seamless experiences.
Wearable Integration
- Smart glasses (Meta Ray-Ban, Apple Vision) enabling mobile AR.
AI + AR/VR Fusion
- AI-driven personalization in immersive experiences.
5G & Edge Computing
- Faster networks powering low-latency AR/VR apps.
Everyday Utility
- AR for navigation, VR for collaboration, XR (extended reality) for hybrid work.
Conclusion
AR and VR are reshaping mobile app development, moving from entertainment to practical, everyday applications. As devices become more powerful and affordable, immersive experiences will no longer be optional — they will be expected.
For developers, the future lies in combining AR/VR frameworks, AI personalization, and 5G-powered performance to deliver apps that go beyond screens into fully immersive experiences.
In short: AR and VR aren’t the future of mobile apps — they’re the present. Developers who embrace them now will lead the next generation of mobile innovation.

